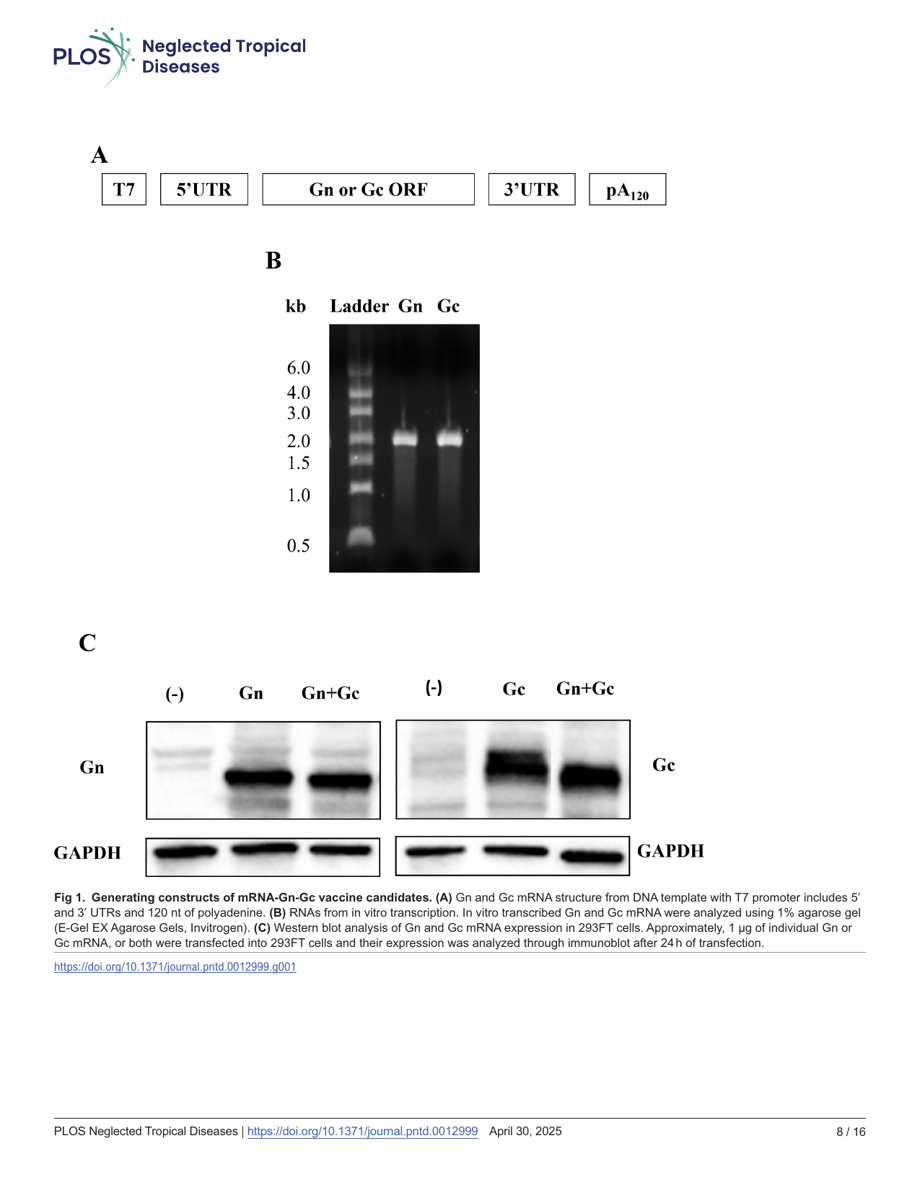
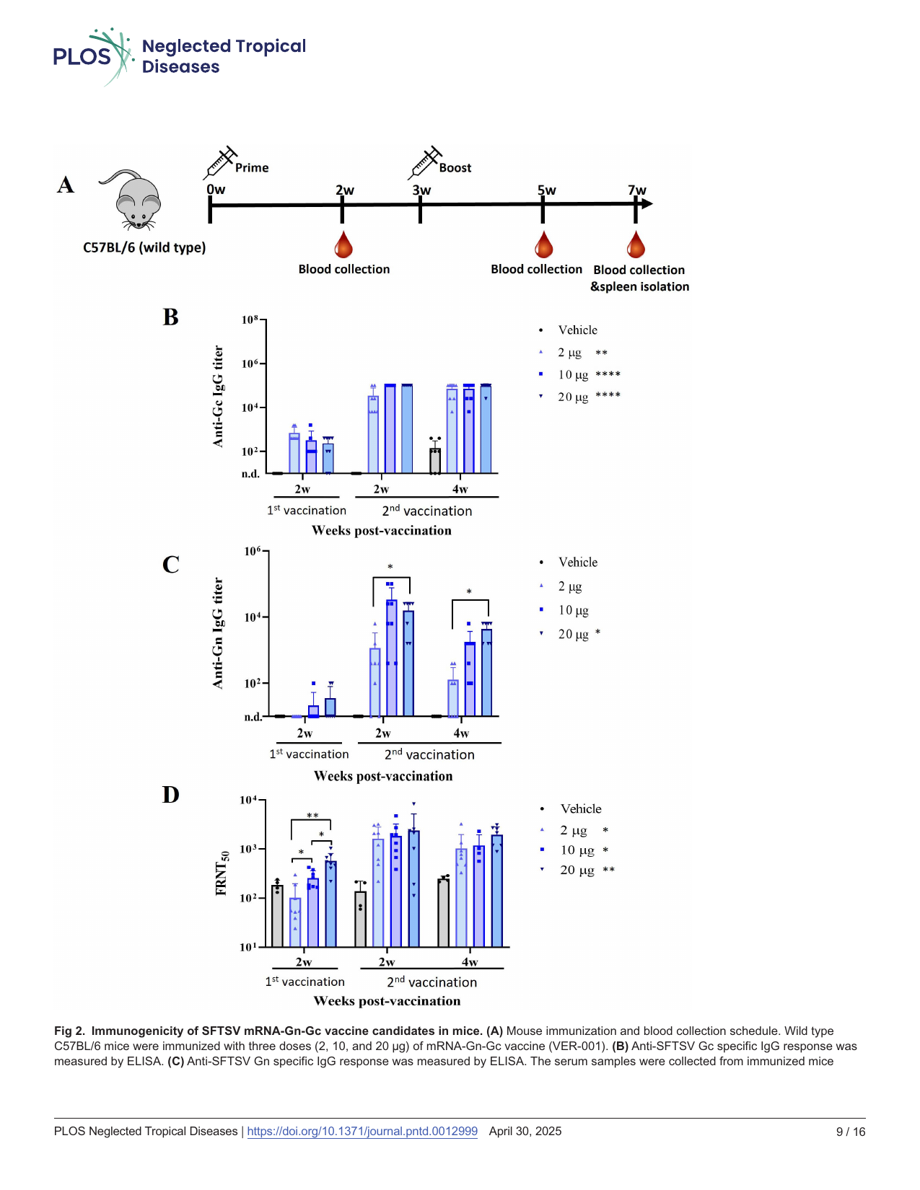
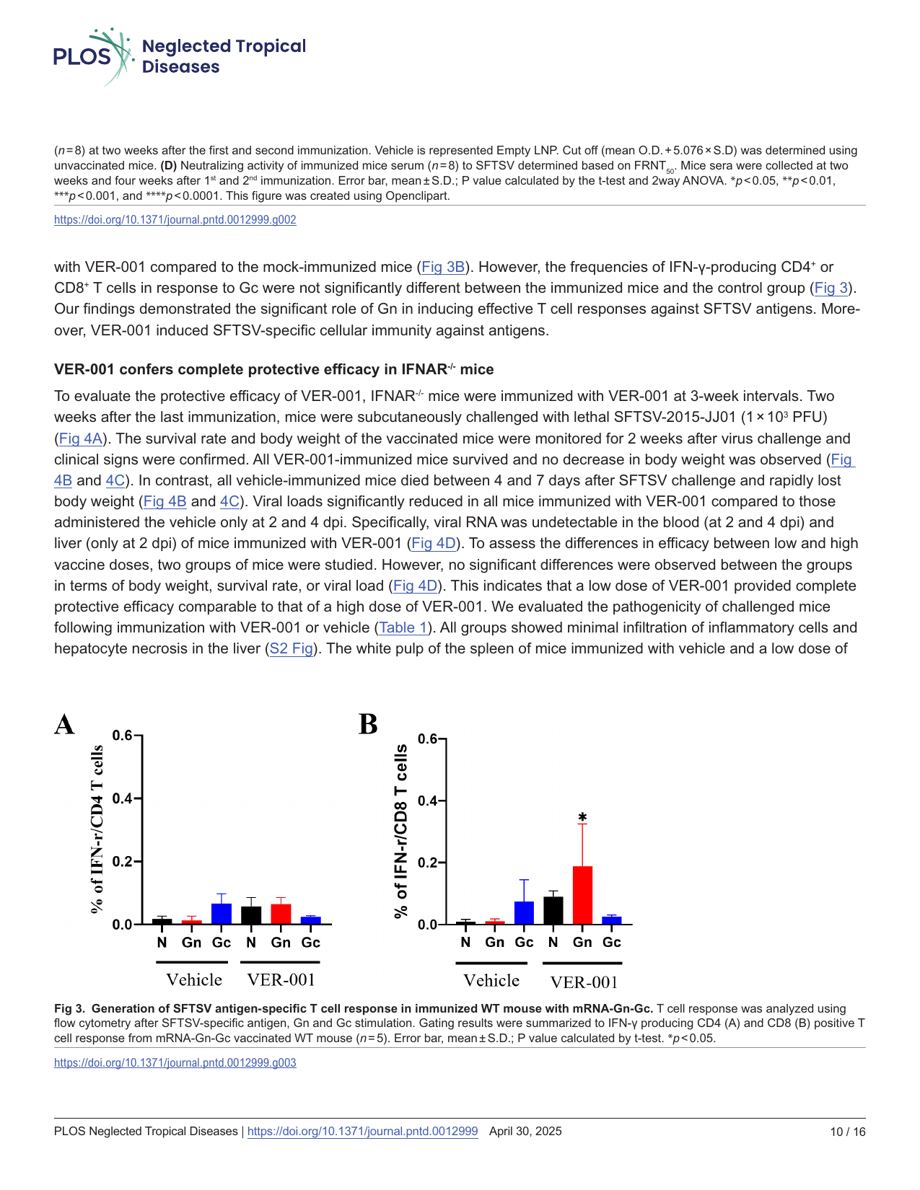
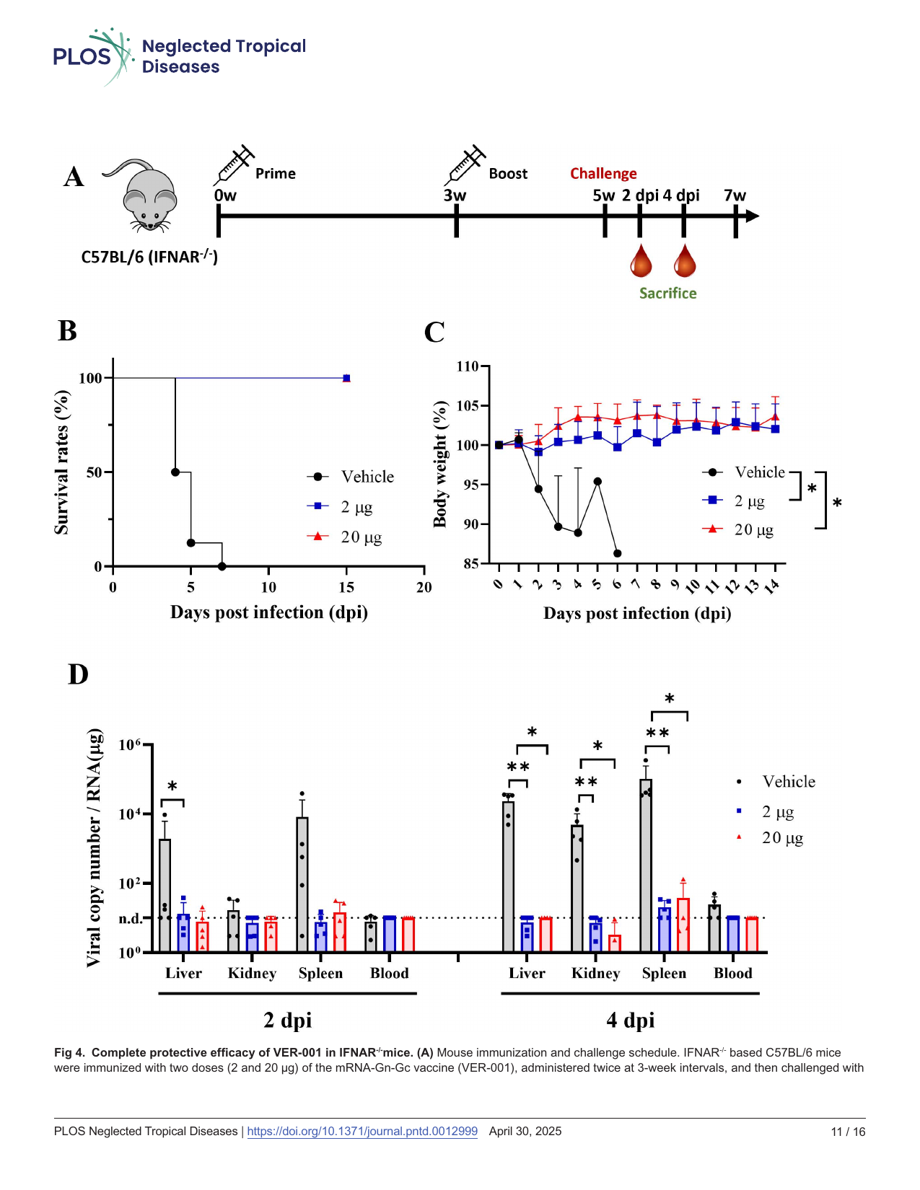
Press Release
Vernagen and US CDC exchanged a letter of intent for the co-development of Heartland Virus mRNA vaccine (3/2023)
Heartland virus (HRTV) is an emerging tick-borne pathogen that is prevalent mainly in the central and southeastern regions of the United States ranging from Illinois to Florida and from North Carolina to Kansas, although HRTV seropositive cases among wild deer have also been reported in New York (Long Island), Vermont, and Maine. Lone star ticks are known as a main carrier of HRTV, and HRTV antibodies were identified in various wild animals including deer, racoons, and moose.
The typical symptoms of HRTV infection include fever, fatigue, and muscle/joint pain, but severe cases, especially in older patients, can be lethal with significant loss of white blood cells and platelets, leading to organ failure. As of November 2022, more than 60 cases of Heartland virus disease have been reported from states in the Midwestern, Northeastern, and Southern United States. However, a CDC study of blood donations in 2019 reported that approximately 1 percent of the total donor blood tested seropositive for HRTV. This indicates a likelihood of under-reporting in populations in the affected areas. Currently, no therapeutic treatments and vaccines against HRTV infection are available, and only clinical supports for the individual symptoms of HRTV infection are recommended.
Under their collaboration, Vernagen, LLC will supply the HRTV mRNA vaccine to CDC's Arboviral Diseases Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases. CDC will conduct the animal/preclinical investigations to evaluate its immunogenicity and protection efficacy against HRVT infection using the HRTV animal model that was previously developed by CDC. The initial agreement officially permits this preclinical joint research investigation to commence through the Cooperative Research and Development Agreement program of CDC that will support the collaborative investigations between this Atlanta-based mRNA vaccine biotech and CDC upon approval.